The New York State Department of Labor today released preliminary local area unemployment rates for August 2023. Rates are calculated using methods prescribed by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The State’s area unemployment rates rely in part on the results of the Current Population Survey, which contacts approximately 3,100 households in New York State each month. To recap last week’s statewide press release, New York State’s seasonally adjusted unemployment rate held constant at 3.9% in August 2023.
Local Area Unemployment Rates* (%)
August 2022 and August 2023
(Not seasonally adjusted)
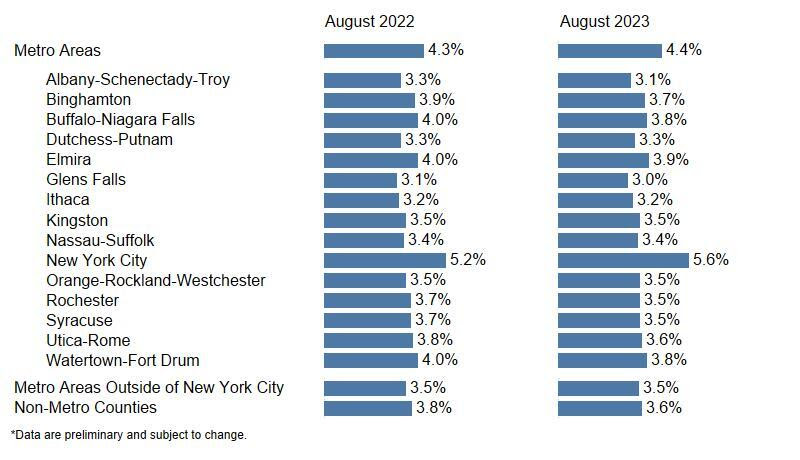 The data in the preceding table are not seasonally adjusted, which means they reflect seasonal influences (e.g., holiday and summer hires). Therefore, the most valid comparisons with this type of data are year-to-year comparisons of the same month, for example, August 2022 versus August 2023. Labor force data for the current month are preliminary and subject to revision as more information becomes available the following month. Revised estimates for prior months are available at: https://dol.ny.gov/local-area- Labor force statistics, including the unemployment rate, for New York and every other state are based on statistical regression models specified by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. These are the most up-to-date estimates of persons employed and unemployed by place of residence. Estimates are available for New York State, labor market regions, metropolitan areas, counties and municipalities with population of at least 25,000. |
 |
 |

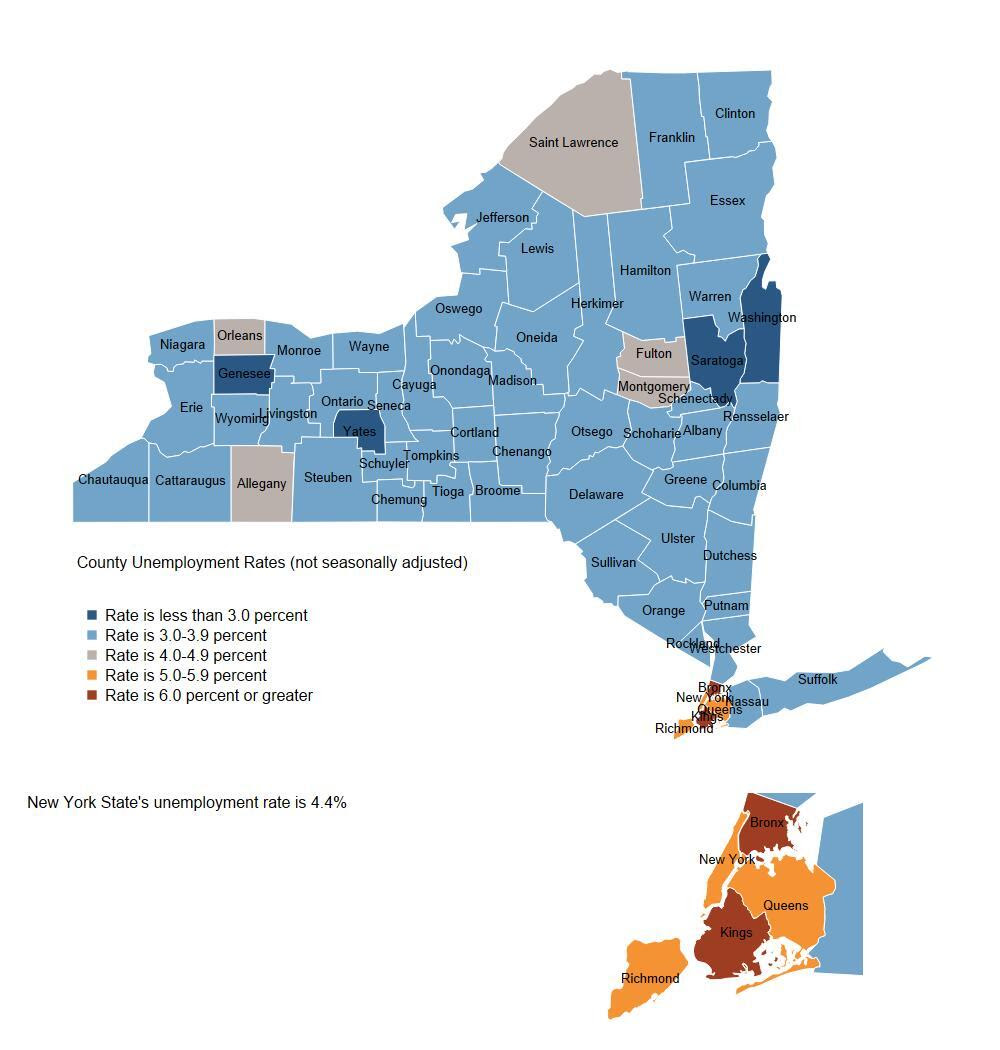
Unemployment Rates By County,
New York State,
August 2023
 Jobs and Unemployment Fact Sheet This fact sheet conveys important technical information that will contribute to a better understanding of labor force data (“household survey”), including resident employment/unemployment rates, and jobs by industry data (“business survey”), which are presented in the New York State Department of Labor’s monthly press release. State Unemployment Rates Based on Regression Model Beginning with data for January 1996, unemployment rates for New York State and all other states (as well as New York City and the City of Los Angeles) have been estimated using time-series regression statistical models developed by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Advantage of Regression Model Use of a time-series regression model reduces the month-to-month variation in unemployment rates and resident employment by reducing variation caused by sampling errors and other components of statistical noise (irregularities). Benchmarking of Estimates Once each year, labor force estimates, such as civilian labor force and the unemployment rate, are revised to reflect updated input data including new Census Bureau populations controls, newly revised establishment jobs data and new state-level annual average data from the Current Population Survey (CPS). As part of this procedure, all state figures are reviewed, revised as necessary and then re-estimated. This process is commonly referred to as “benchmarking.” Changes in Methodology Labor force estimates are now produced with an improved time-series regression model, which utilizes “real-time” benchmarking. “Real-time” benchmarking reduces end-of-year revisions, which also means that major economic events will be reflected in a more timely manner in state labor force estimates. In addition, the new methodology includes an updated way of estimating for sub-state areas (e.g. counties, metro areas) the number of unemployed who are new entrants or re-entrants into the labor force. This change in methodology will result in lower unemployment rates in some areas and increased rates in others. Unemployed and UI Beneficiaries The estimate of the number of unemployed includes all persons who had no employment during the reference week (the week including the 12th of the month), were available for work, except for temporary illness, and had made specific efforts to find employment sometime during the 4-week period ending with the reference week. Unemployment insurance (UI) beneficiaries include those who apply for and qualify for UI benefits. Consequently, the estimate of the number of unemployed and the number of UI beneficiaries do not necessarily move in tandem. Jobs Data Jobs data are obtained from a separate joint federal-state survey of business establishments. The survey, called the Current Employment Statistics of Establishments, samples establishments in New York State. It excludes self-employed workers, agricultural workers, unpaid family workers and domestic workers employed by private households. This data represents a count of jobs by place of work. Data for each month is revised the following month as more complete information becomes available. The New York State Department of Labor is an Equal Opportunity Employer/Program. |

